Production Technology of Multi-Lumen Catheters
Multi-lumen catheters are specialized medical devices used in various medical treatments, and their design and production processes have high technical requirements. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the production process of multi-lumen catheters, focusing on the technical highlights and the application of relevant equipment to help readers better understand the production process of these devices.
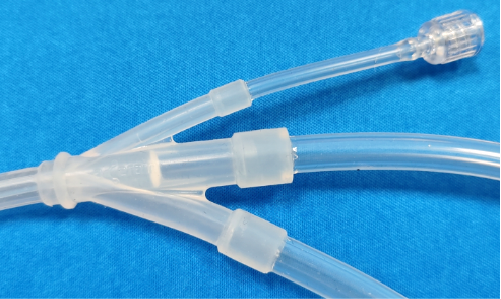
Multi-lumen catheters are medical devices used for surgical or therapeutic procedures in different medical fields. Their primary function is to provide stable passages during surgery or treatment. These catheters are available in different sizes, such as Ø6 (18FR) and Ø8 (24FR), which are designed to meet various clinical needs. The catheter design includes multiple components such as the main tube body, branch tube bodies, trifurcated branch connectors, balloons, and tips, which are assembled through various process flows.
Production of Main Tube and Branch Tubes
- Material Preparation: The production of the main tube and branch tubes uses a combination of solid rubber compound and vulcanizing agents. This material combination ensures that the catheter has good flexibility and durability.
- Rubber Compounding and Extrusion: The rubber compound is mixed with vulcanizing agents and processed in a rubber compounding machine. The extrusion process is then carried out using an extruder and extrusion molds to shape the rubber into the desired form. The design of the extrusion molds is critical for the shape and dimensional accuracy of the catheter.
- Inspection and Cutting: After extrusion, the tubes are visually inspected for defects. Once confirmed to be free of defects, they are cut to the required length using cutting tools.
- Secondary Vulcanization: The cut tubes undergo a secondary vulcanization process through baking to further enhance their physical properties.
Production of Trifurcated Branch Connectors and Positioning Rubber Balls
- Material Preparation: The production of trifurcated branch connectors and positioning rubber balls also uses a combination of solid rubber compound and vulcanizing agents, in addition to silicone sealant and inspection fixtures.
- Compression Molding: The compounded rubber is placed into compression molds for shaping. The precision of the compression molds directly affects the size and shape of the components.
- Baking Vulcanization: The molded components are then baked to vulcanize them, ensuring that their physical properties meet the required standards.
- Adhesive Application and Leak Testing: For trifurcated branch connectors, adhesive application is necessary, followed by leak testing to ensure their watertight integrity.
Assembly of Balloons and Tips
- Material Preparation: Both balloons and tips are purchased components that require cleaning and inspection.
- Assembly Process: The assembly of balloons includes compression molding, cutting, installation of sleeves, adhesive application (three times), and inflation testing. The assembly of tips involves cleaning, installation of sleeves, adhesive application (three times), and inflation testing.
- Quality Control: During the assembly process, it is essential to strictly control the quality of adhesive application and the accuracy of inflation testing to ensure the sealability and safety of the products.
Other Processes
- Punching: Holes are punched into the catheter using tools such as punch knives, pliers, tube placement fixtures, and pads.
- Screen Printing and Transfer Printing: Specialized silicone ink is used for screen printing or transfer printing, followed by baking to cure the ink.
- Valve Installation: Purchased valves are installed into the catheter using tube expansion fixtures.
Mold Design
Vulcanization Process
Adhesive Process
Air-Tightness Testing
Equipment List