Cold Runner Molds vs. Hot Runner Molds: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to injection molding, two common types of molds are cold runner molds and hot runner molds. Both have their unique advantages and applications, but they differ significantly in design, operation, and efficiency. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between cold runner molds and hot runner molds to help you understand which one is best suited for your manufacturing needs.
What is a Cold Runner Mold?
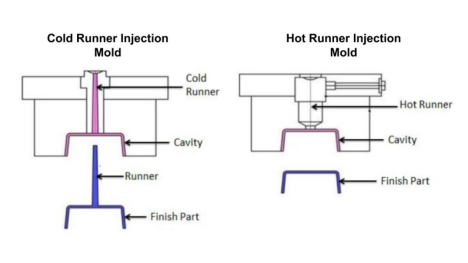
A cold runner mold is a traditional type of injection mold that features a runner system through which molten plastic travels from the sprue to the individual cavities. The runner system includes the sprue, runners, and gates, which are all part of the mold’s structure. After the plastic is injected into the mold, it cools and solidifies in both the cavities and the runner system. When the mold is opened, the solidified plastic parts, along with the runners and sprue, are ejected. The runners and sprue must then be separated from the finished parts, often resulting in material waste.
Key Features of Cold Runner Molds:
- Design: Typically consists of two or three plates with a fixed runner system.
- Operation: Molten plastic is injected into the mold, filling the cavities and runners. The plastic then cools and solidifies.
- Material Waste: Significant waste in the form of runners and sprues, which must be removed and often discarded or recycled.
- Cost: Lower initial cost due to simpler design and manufacturing.
- Applications: Suitable for small to medium production runs, especially when material cost is not a significant concern.
What is a Hot Runner Mold?
A hot runner mold, on the other hand, features a heated runner system that keeps the plastic in a molten state throughout the molding process. This system includes heated nozzles, manifold plates, and temperature controllers to maintain the plastic’s temperature. The molten plastic is injected directly into the cavities from the heated runner system, eliminating the need for solidified runners and sprues. As a result, there is minimal material waste, and the production process is more efficient.
Key Features of Hot Runner Molds:
Design: More complex, with heated nozzles, manifold plates, and temperature controllers.
Operation: The plastic remains molten in the runner system, allowing for continuous injection into the cavities.
Material Waste: Minimal waste, as the plastic in the runners remains molten and is reused in subsequent cycles.
Cost: Higher initial cost due to the complex design and the need for precise temperature control.
Applications: Ideal for large production runs and applications where material waste and production efficiency are critical.
Cold Runner Molds vs. Hot Runner Molds: A Comparison
Let’s take a closer look at the differences between cold runner molds and hot runner molds in terms of design, operation, material usage, production efficiency, product quality, and cost.
| items | cold runner mold | hot runner mold |
| Runner State | Solidifies and cools, forming waste material | Remains molten, no waste material |
| Material Waste | Higher (requires processing of sprue waste) | Minimal or none |
| Mold Cost | Low | High (due to heating system and complex temperature control) |
| Production Cycle | Longer(requires cooling of runners) | Shorter (only cavity cooling required) |
| Product Appearance | May have gate marks | Smaller gate marks, better appearance |
| Applicable Scenarios | Small batch, low-cost production | Large batch, high-precision, or high-value-added production |
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between cold runner molds and hot runner molds depends on several factors, including the type of material, production volume, and cost considerations. Here are some guidelines to help you make the right decision:
- Cold Runner Molds: Suitable for small to medium production runs, especially when the material cost is not a significant concern. They are also a good choice for materials that are difficult to process in hot runner systems.
- Hot Runner Molds: Ideal for large production runs and applications where material waste and production efficiency are critical. They are best suited for materials that can be easily processed in a molten state, such as thermoplastics.
Finally, We hope this guide has helped you understand the key differences between cold runner molds and hot runner molds. If you have any further questions or need assistance with your injection molding projects, feel free to reach out to us. Our team of experts is here to help you every step of the way.